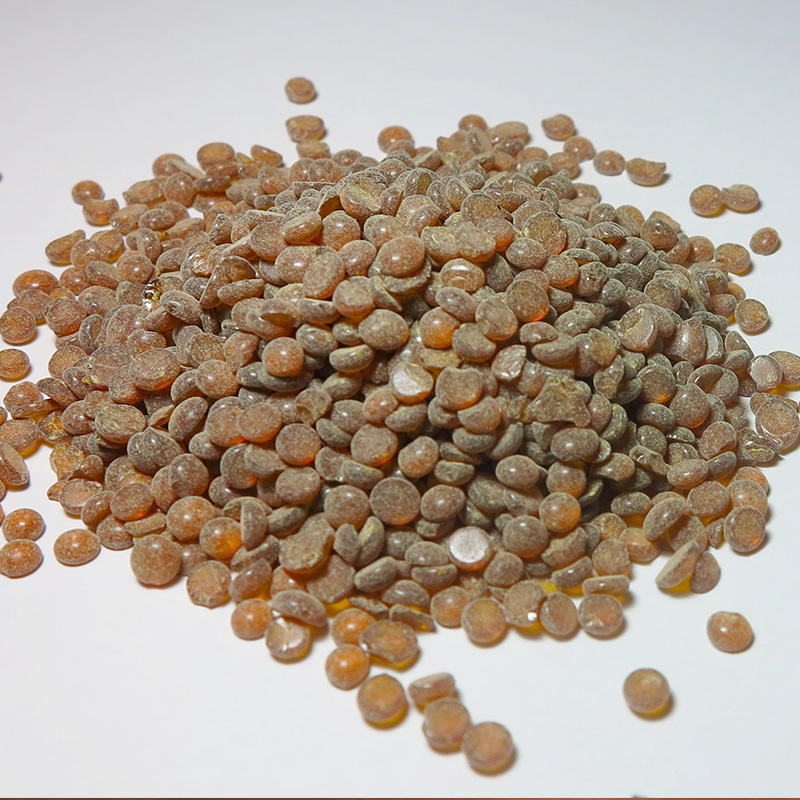
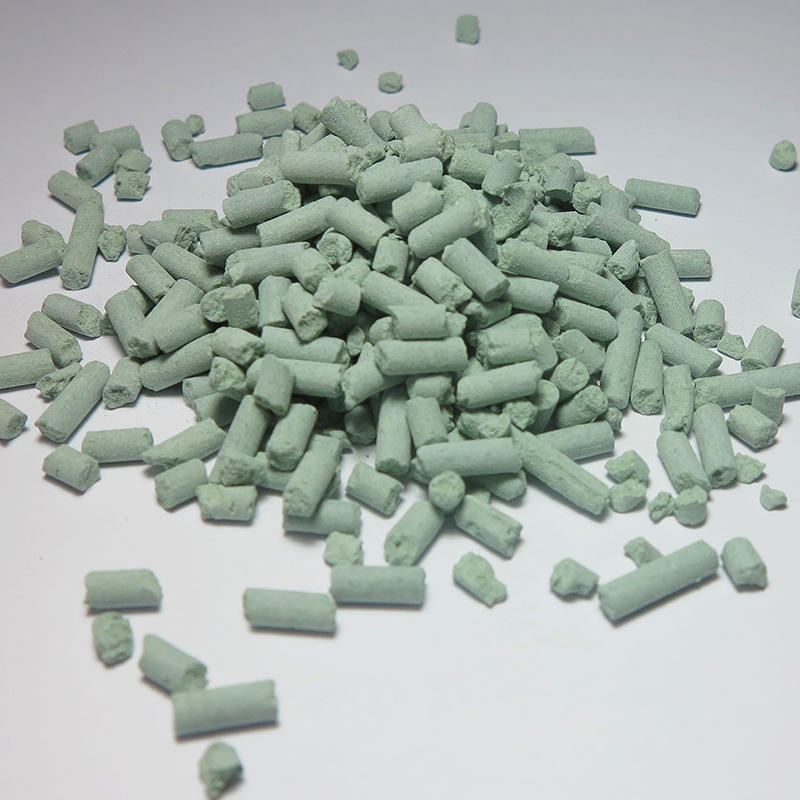
Mercaptans are one of the main raw materials for the synthesis of vulcanizing agents. Mercaptans can react with oxygen under the action of hydroxides of alkali metals and alkaline earth metals to obtain vulcanizing agents. It can also be mixed with elemental sulfur as a raw material to synthesize an organic vulcanizing agent under the action of a basic catalyst. The earliest catalysts used in this synthesis route are amines, alkanolamines, thiolates, alcoholates, and inorganic bases. However, the use of these catalysts has disadvantages such as low yield, low product purity, and unpleasant odor. Therefore, the study of new catalysts is the focus of this synthetic route. Substituting alkylene oxide for the olefin oxide group in the composition further improves the yield of polysulfides, the chromaticity becomes lower and the chromaticity is less than or equal to, and the product has no unpleasant odor or turbidity. Some scholars began to use resin as a catalyst. It is proposed to use an organic anion exchange resin containing a quaternary ammonium hydroxide group or a tertiary amine group as a catalyst. This resin exists in the form of beads or bidentate in the reaction system, has low solubility and is easy to recycle, but the organic vulcanizing agent The yield is not high. In order to solve this problem, a study was carried out, and a resin with one or one form was proposed as a catalyst. This resin has a highly cross-linked macroporous structure. Compared with gel-type resins, this resin has greater catalytic activity during the reaction and can effectively increase the yield of organic vulcanizing agents. Aretz proposed the use of polystyrene-divinylbenzene-resin containing muscle groups and mitochondria as a catalyst. This resin can react low-level organic disulfides and polysulfides with elemental sulfur to obtain high-level polysulfides. In addition, the resin can also react high-level organic vulcanizing agents with mercaptans to obtain lower-level polysulfides. The resin exists in the reaction liquid in the form of pellets or beads, and is easily separated after the reaction is completed. Fremi has developed a polystyrene-divinylbenzene-based resin grouped with ethylenediamine or polyvinylpolyamine. This catalyst can effectively increase the conversion rate of the reactants. The application of these new catalysts not only effectively increases the sulfur content of the vulcanizing agent, but also expands the range of raw materials. More importantly, it overcomes the shortcomings of traditional catalysts such as low yield, low product purity, and unpleasant smell. However, the synthesis of the new catalyst is complicated, the raw material cost is too high, and some raw materials are not easy to obtain and not easy to industrialize application.
2. With olefins and sulfur
The reaction mechanism of sulfur and olefins to synthesize organic vulcanizing agents is that molecules in the presence of a catalyst, at a certain temperature, the ring breaks to form linear molecules, which exist in the system in the form of free radicals, and react with olefins to generate organic vulcanizing agents. The most widely used synthesis of organic vulcanizing agents from elemental sulfur and olefins has also been highly valued by scholars. The patent discloses the use of sulfur and isobutylene as raw materials to synthesize an organic vulcanizing agent. The organic vulcanizing agent synthesized by this method has low odor, few by-products and no pollution. However, this method has strict requirements on reaction conditions and high cost, which is not suitable for industrial applications. The patent discloses the direct reaction of elemental sulfur and olefins to synthesize a vulcanizing agent. The process of synthesizing organic vulcanizing agent by this method is simple, but there are many by-products, unpleasant odor, and some by-products are corrosive, causing serious damage to equipment Damage. In response to the above problems, Sun Laiyin proposed to use isobutylene as a raw material to synthesize an organic vulcanizing agent under high pressure. This method has few by-products, low odor, almost no pollution to the environment, high sulfur content, but isobutylene is not easy to obtain, and the price is relatively high. Ji Yonggang proposed to use butene, which is a byproduct with a low utilization rate in the separation-butene process, as the raw material for the synthesis of vulcanizing agent. This method has a simple synthesis process, cheap and readily available raw materials, and greatly reduces production costs. Although a single olefin is used as a raw material to synthesize an organic vulcanizing agent, several compounds with different sulfur content can be obtained, but there is still a problem of excessive heat release when the catalyst is pre-sulfided. In order to solve this problem, many scholars propose to use a mixed vulcanizing agent to presulfide the catalyst, but the proportion of each component of the mixed vulcanizing agent is not easy to determine, the cost is high, and there are many by-products produced during the presulfiding. Yu Shouzhi uses the distillate oil produced by wax cracking as the raw material for the synthetic organic vulcanizing agent. This method solves the problem of concentrated heat release of a single polysulfide during pre-vulcanization, but the product has large anvils and poor fluidity, which is required before pre-vulcanization. Dilute it. Wang Deqiu proposed to use distillate oil as a raw material to synthesize an organic vulcanizing agent. The organic vulcanizing agent synthesized by this method has high sulfur content, low toxicity, small tolerance, and good fluidity. The synthetic route of sulfur, hydrogen sulfide and olefins as raw materials uses elemental sulfur, olefins and hydrogen sulfide as raw materials to prepare organic vulcanizing agents.
3. Olefins, sulfur halides
Synthesizing vulcanizing agents with olefins and halogenated sulfur as raw materials is a common method in my country's industry. Halogenated sulfur and olefins generate halogen-containing organic vulcanizing agent in the presence of a catalyst, and then undergo a dehalogenation process to obtain the organic vulcanizing agent. At the beginning of the century, Chinese scholar Huang Jinxia proposed to use sulfur chloride and isobutylene as raw materials to synthesize organic vulcanizing agent. The organic vulcanizing agent synthesized by this method has high sulfur content, high stability and low corrosivity, but this method is used in the synthesis of organic vulcanizing agent. During the production process, a large amount of waste gas, waste water and waste liquid will pollute the environment. In recent years, many documents have successively reported the improved method of the synthesis route. For example, Yang Jingpei proposed to synthesize the organic vulcanizing agent containing impurities in two steps under a closed pipeline, and then obtain the pure organic vulcanizing agent through the steps of separation, dehydration, and purification. The process is carried out in a closed pipeline, which avoids the pollution of waste gas and waste liquid to the environment. However, this method has a complicated synthesis process and high equipment requirements, and is not suitable for industrial applications. Zhou Bo proposed the use of two sulfur additions and dechlorination methods to treat sulfurized isobutylene containing chlorine atoms. This method simplifies the process steps and saves costs, but the production cycle is long. Qi Xiangyang proposed to recycle the sulfur-containing waste liquid produced by the second-step sulfurization and dechlorination reaction for the next first-step sulfurization and dechlorination reaction, which not only reduces the discharge of waste liquid, but also saves production costs. The new synthesis process solves the "three wastes" problem and reduces production costs, but the equipment investment is large, the production cycle is long, and the operation process is complex, making it difficult to realize industrial applications.


 English
English Português
Português Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体










