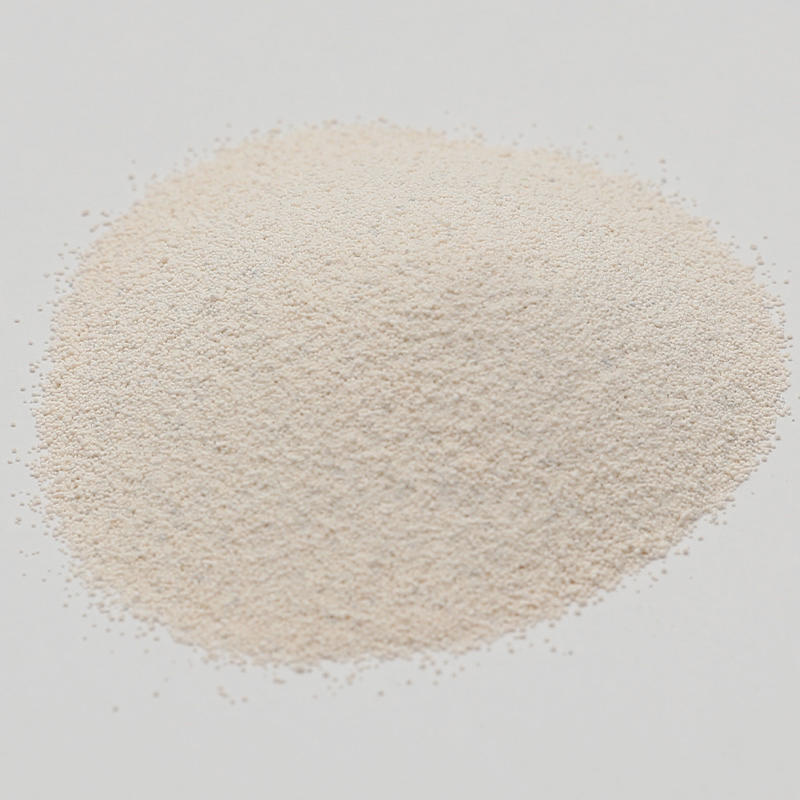
Borax is also divided into powder and granular form, and fine-grained borax is the best. Borax is divided into two grades according to its strength. 10 moles of borax has 10 water molecules, which is called grade 10 water borax. 5 moles of borax has 5 water molecules, which is called grade 5 water borax. The concentration of 5 moles of borax is higher. 0.35 kg of 5 moles of borax is equivalent to 0.454 kg of 10 moles of borax. If the same amount of two kinds of borax is used incorrectly, the consequences will be serious. If borax is added to raw starch and water emulsion, and then the mixture is heated, the starch swells quickly after absorbing water and becomes more viscous than without borax.
The amount of borax added has a certain limit, otherwise, it will affect the expansion of starch, the gelatinized paste will become brittle, and it will be in a powdery state when dry.
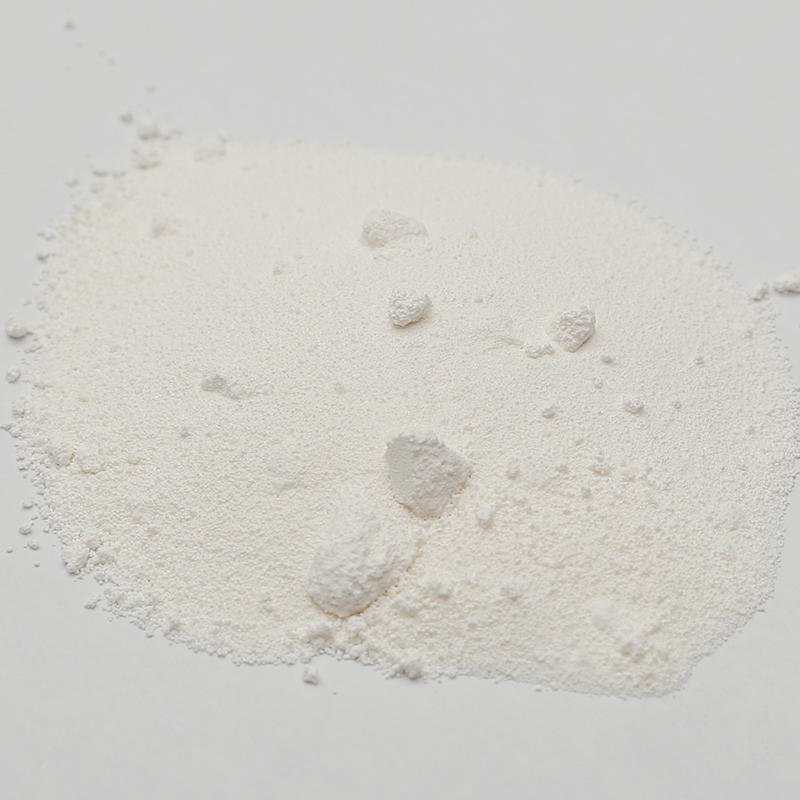
As long as the caustic soda contains 76% sodium oxide, commercial grade without additives, crumbs or flakes can be used. The composition is equivalent to 98% sodium hydroxide. Caustic soda absorbs moisture in the air and reduces its strength. Therefore, if the packaging barrel is damaged, it should not be used. After opening the lid of the barrel to take the material, the lid of the barrel should be tightly closed immediately.
Caustic soda
Caustic soda is a strong alkali that can cause severe burns to the skin in a dry state or when dissolved in water. Wear a mask and rubber gloves when handling caustic soda, and prepare a bottle of vinegar at any time to treat the skin contaminated by caustic soda immediately. Caustic soda will smoke when it is dissolved in water. Do not inhale the smoke that comes out because the smoke is toxic.
Caustic soda is added to the emulsion of raw starch and water, and the mixture is heated to reduce the temperature of starch swelling and gelatinization. According to this feature, the amount of caustic soda added can be used to precisely control the temperature of starch swelling and gelatinization. However, too much addition will cause the gelatinized particles to split, reduce the viscosity, and gelatinize the raw starch in the paste in advance.
Formaldehyde
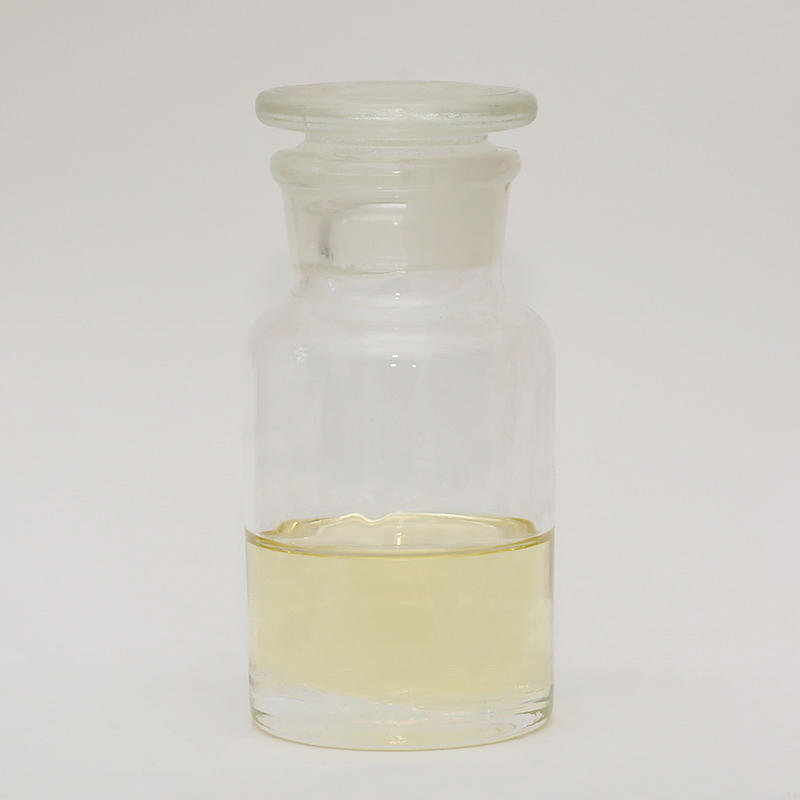
Formaldehyde is in the state of 37% aqueous solution and is measured according to the volume or wet weight specified in the formula. Formaldehyde is used in general adhesives for corrosion protection. It is used as a chemical crosslinking agent in some waterproof adhesive formulations. Wear protective equipment when handling formaldehyde, because formaldehyde has a strong irritation to the eyes and skin, so you should absolutely avoid inhaling it.
Water-resistant adhesive
The difference between water-resistant adhesives and ordinary adhesives is usually that they contain more raw starch, less caustic soda, and contain no or little borax. Of course, water-resistant adhesives add a certain amount of waterproofing agent. There are many water repellents that can be used, all of which are water-soluble resins. After this type of resin is chemically crosslinked with formaldehyde, it will become a water-insoluble and water-resistant adhesive when heated on the paste line.
Most water-resistant adhesives have a certain life span. Some gradually thicken over time, even under agitation. Some machinery has good operational performance, but the water resistance is greatly reduced. Therefore, the adhesive must be used as soon as possible after it is prepared.


 English
English Português
Português Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体










