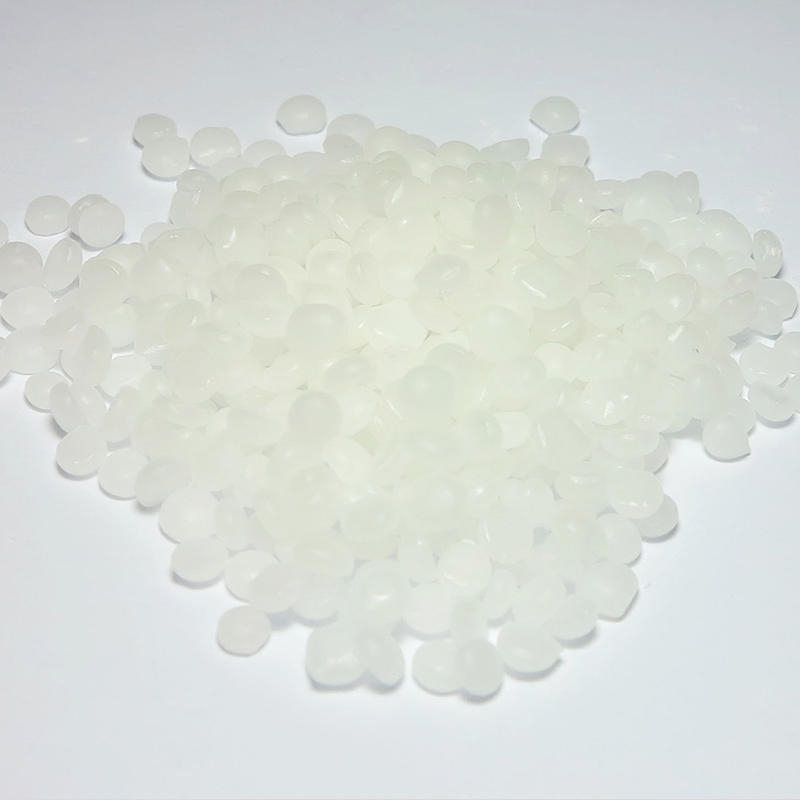
1. Series Introduction
There are six commonly used rubber accelerators:
Sulfonamides: CBS (N-cyclohexyl-2-benzothiazole sulfenamide), TBBS (N-tert-butyl-2-benzothiazole sulfenamide), NOBS (N-oxydiethylene 2-benzothiazole sulfenamide), DZ (N,N'-bicyclohexyl-2-benzothiazole sulfenamide)
Thiurams: TMTD (tetramethylthiuram disulfide), TMTM (tetramethylthiuram monosulfide), TETD (tetraethylthiuram disulfide), DPTT (pentamethylene thiuram hexasulfide) Lamb)
Thioformates: ZDC (zinc diethyl dithiocarbamate), BZ (zinc dibutyl dithiocarbamate), PZ (zinc dimethyl dithiocarbamate),
Guanidines: D (Diphenylguanidine)
other
2. Purpose
Rubber accelerator is the aftereffect accelerator of natural rubber, butadiene rubber, isoprene rubber, styrene butadiene rubber and reclaimed rubber. It is usually used in the manufacture of cables, tapes, rubber shoes, inner tubes, bright color products, etc., especially suitable for alkali-containing products. Strong carbon black compound. It is safe at operating temperature, has strong scorch resistance, fast vulcanization speed, and high tensile strength, which can increase the use ratio of synthetic rubber. With low toxicity and high efficiency, it is an ideal substitute for NOBS. It has excellent comprehensive performance and is called a standard accelerator. It is widely used in the production of radial tires. It can be used together with aldehyde amine, guanidine and thiuram accelerators. When used together with anti-scorching agent PVI, it can form a good vulcanization system. Mainly used in the production of tires, rubber shoes, hoses, tapes, and cables.


 English
English Português
Português Español
Español русский
русский 中文简体
中文简体










